Concours vidéo iAds pour les collégiens 2025
Le projet européen iAds coordonné par l’équipe d’Eric Kremer a lancé la deuxième édition du concours vidéo pour les élèves de 3ème des collèges montpelliérains.
Pour plus d’information, visitez la page dédiée au concours.

EKL coordinates project iAds – “Intelligent design of adenovirus vectors”
For the last 20 years, the Kremer lab has had a broad interest in adenovirus biology. Adenoviruses are nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA pathogens with a genome size of 28 – 42 kb. To date, ~70 human and > 150 nonhuman adenovirus types have been described. We focus on human and canine adenoviruses (CAV-2) vectors.
OUR PRINCIPLE AREAS OF INTEREST ARE:
1.Understanding the function of CAR, the coxsackievirus adenovirus receptor, in the healthy and disease brain, and during adenovirus trafficking.
As the name suggests, CAR was originally identified as an attachment molecule for coxsackie B viruses and some adenoviruses, including canine adenovirus type 2 (CAV-2) vectors, whose transduction efficacy is CAR dependent. CAR is a single-pass transmembrane protein belonging to the CTX subfamily of the Ig-super family. CAR function is best characterized in epithelial cells where it participates to the maintenance of tight junctions. Although a role for CAR in brain development has been hypothesized and a function in regulating axonal growth reported, its role in the adult brain is largely uncharacterized. In this context, understanding CAR’s biological function, as well as the impact of its loss of function and distribution in the CNS is indispensable for both fundamental and applied neurobiology studies.
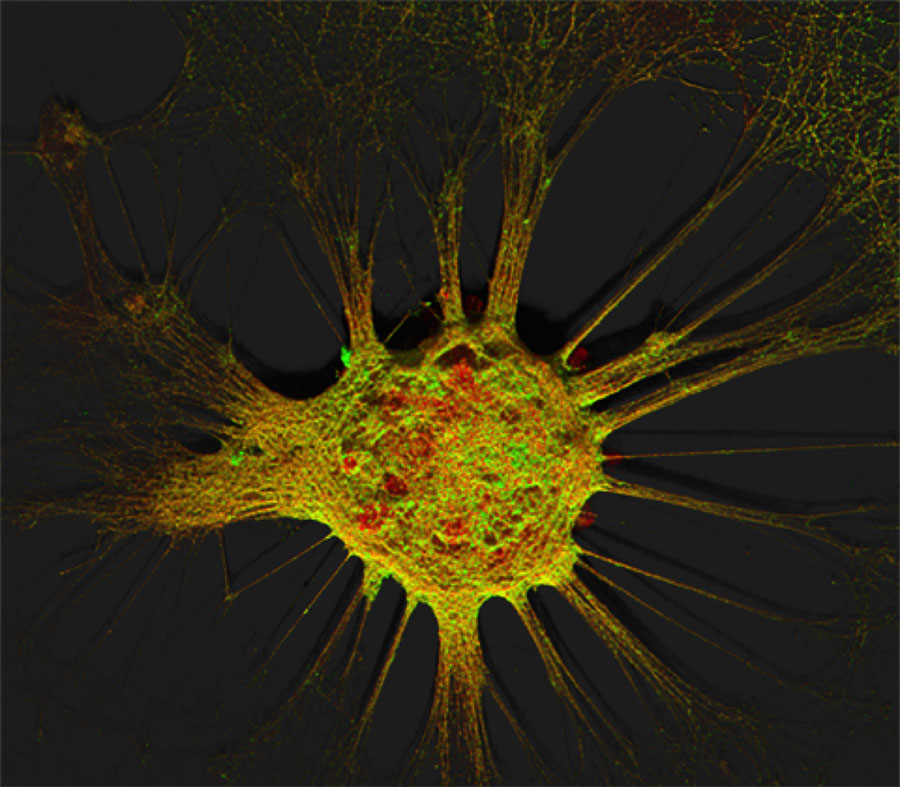
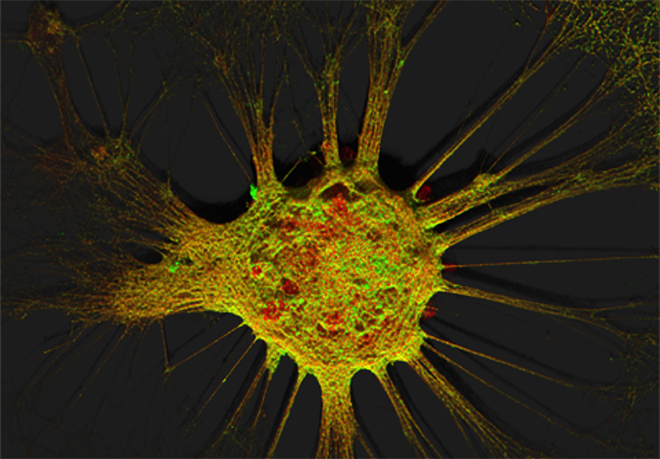
Figure 1. Mouse hippocampal neurons at day in vitro 15 (DIV 15). Cells were labelled for mouse coxsackie- and adenovirus receptor using a goat anti-mCXADR (R&D systems) detected with a donkey anti-goat Alexa 488 and a rabbit anti-CAR (gift from Joseph Zabner) detected with an donkey anti-rabbit Alexa 647. Nucleus were stained using DAPI (blue). Images were acquired using Leica SP5 confocal microscope with 40X 1.4 oil objectives. Serial Z-plan were recorded and images represent z-projection of all 34 plan acquire. (yellow image)
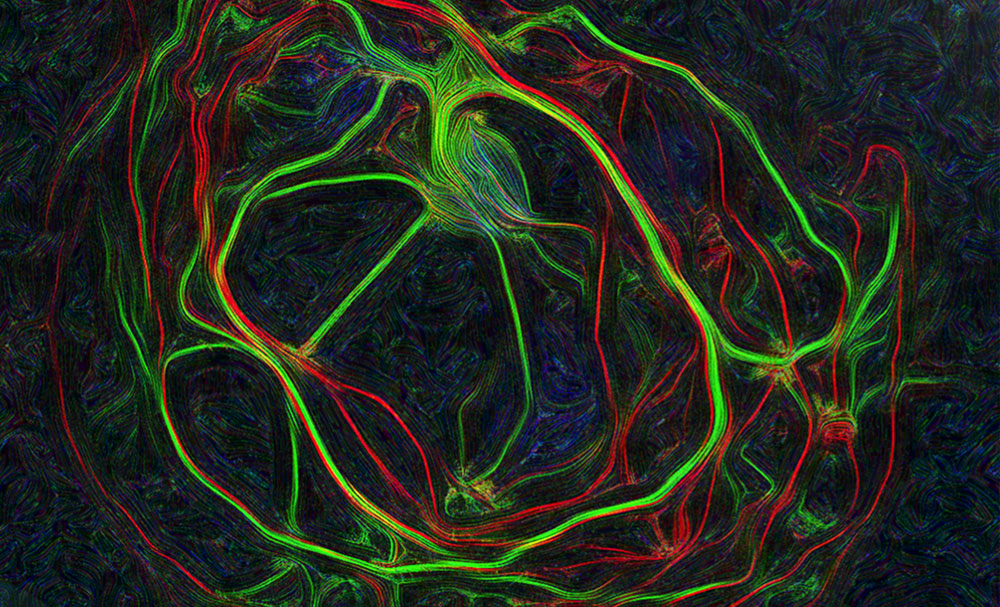
Images represent mouse hippocampal neurons at day in vitro 7 (DIV 7). Cells were labelled for mouse coxsackie- and adenovirus receptor using a rabbit anti-mCAR (Bethyl) detected with a donkey anti-mouse Alexa 555 and a mouse anti-RNA Pol II H5 (Abcam) detected with an donkey anti-mouse Alexa 488. Nucleus were stained using DAPI (blue). Images were acquired using Leica SP5 confocal microscope with 40X 1.4 oil objectives. Serial Z-plan were recorded and images represent overlay from different plan. Images were pseudo-colored CAR in magenta, RNA pol in cyan and DAPI in yellow.
2.Understanding how mononuclear phagocytes, in particular dendritic cells, process and respond to immune-complexed adenoviruses (IC-Ad)
The nearly ubiquitous presence of anti-adenovirus antibodies and memory T cells is due to recurrent and cross-reacting adenovirus infections during childhood. Thus, when Ad-based vectors are used in a host with memory immunity this creates an environment close to a secondary infection in the clinic.
How do IC-Ads and other host factors impact the maturation of antigen-presenting cells (APC)? Our underlying questions encompass the entry and signaling pathways and how the IC-Ads traffic in APC. In our studies we use human dendritic cells to study the interaction of IC-HAd5 and innate immune sensors. Dendritic cells are the major APC in blood and tissue and play a pivotal role in the sensing of infection and activation and re-activation of the adaptive immune response.
IC-Ads triggers several innate immune sensors and induce DC maturation (the virus alone is far less potent). Our aim is to understand the interactions of the IC-Ads during the initial activation and death of DC. Our studies contribute to both fundamental and applied questions in adenovirus biology, vaccination and gene therapy.
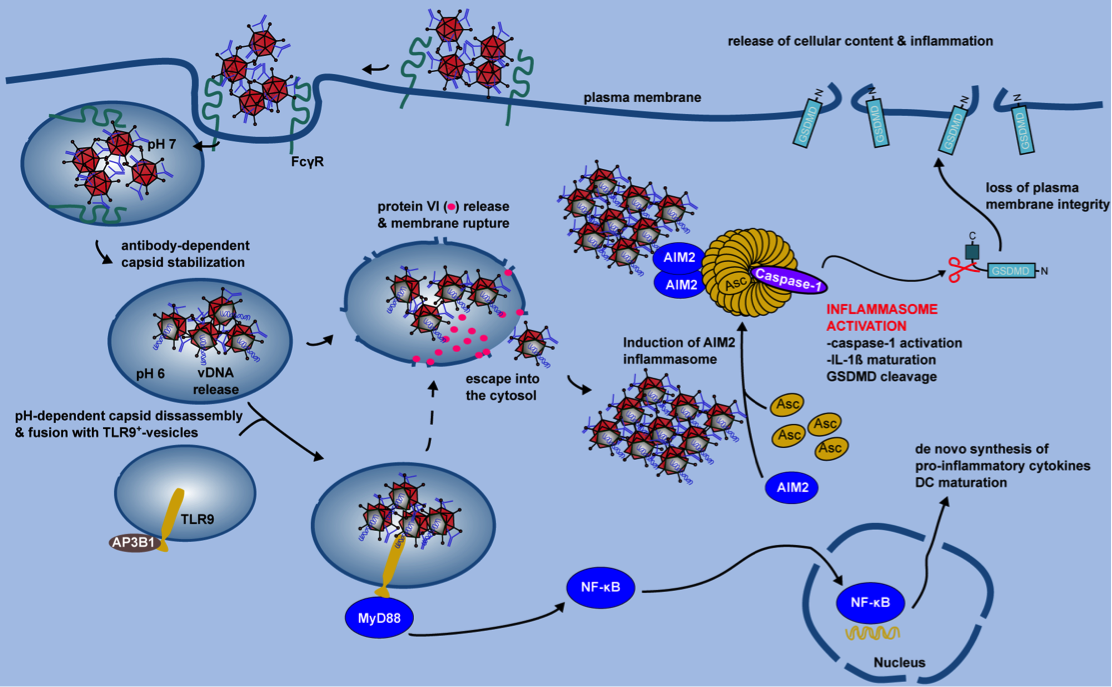
Figure 2. IC-HAdV trafficking and cellular events leading to pyroptotic dendritic cell death.
IC-HAdV are taken up via FcγR-mediated endocytosis and fuse with TLR9+ endolysosomal vesicles because of NAb-dependent capsid stabilization at endosomal pH. At the more acidic pH in lysosome-like vesicles, IC-HAdV begin to disassemble and to release viral DNA, membrane lytic protein VI, and cellular components. TLR9 engagement induces MyD88-NF-κB-dependent de novo expression of TNF and pro-IL-1β. During vesicular DNA sensing, protein VI release from the capsid leads to endolysosomal membrane lysis and IC-HAdV gain access to the cytosol. The cytosolic inflammasome sensor AIM2 interacts with the HAdV-C5 genome and induces inflammasome assembly and activation of caspase 1, and downstream cleavage of pro-IL-1 and GSDMD. Together this leads to pyroptosis of MoDCs.
3.Optimizing CAV-2 vector for gene transfer to the CNS
The Kremer labs created replication-defective and helper-dependent CAV-2 vectors. CAV-2 vectors allow preferential gene transfer to neurons and widespread distribution after injection into the brain. We and others have used them to explore, treat and understand the healthy and diseased CNS.
To respond to the increasing number of requests for CAV-2 vectors, the CNRS BioCampus created a non-profit vector core that provides vectors at cost to colleagues. Please address your questions to cav.2@biocampus.cnrs.fr or see https://www.pvm.cnrs.fr/
Le sous-groupe est composé de Florence Rage, Johann Soret, Pauline Duc et Audrey Moisan
Étude des mécanismes moléculaires de l’atrophie spinale (SMA)
BOURSES DE MASTER INTERDISCIPLINAIRES – IGMM (cnrs.fr)
L’Amyotrophie spinale (SMA) est une maladie génétique rare dont l‘incidence est d’environ 1 pour 6000 naissances. Elle représente la deuxième cause de mort infantile. Cette maladie se caractérise par la mort des motoneurones (MN) alpha de la moelle épinière entrainant une atrophie musculaire sévère allant jusqu’à la paralysie. La mutation et/ou délétion du gène SMN1 entraine une expression très faible de la protéine SMN affectant ainsi le métabolisme des ARN et en particulier leur épissage. Afin d’expliquer la grande vulnérabilité des neurones, un rôle plus spécifique sur le transport des ARNm dans l’axone et leur traduction locale pendant le développement et le maintien de la jonction neuromusculaire (NMJ) a été suggéré.
Notre projet vise à comprendre ces mécanismes dans un modèle humain de motoneurones issus de cellules souches pluripotentes (iPSC) d’individus sains ou de patients atteints de SMA. Ainsi nous récapitulons la maladie et étudions :
- Les défauts d’épissage dans les cellules pathologiques.
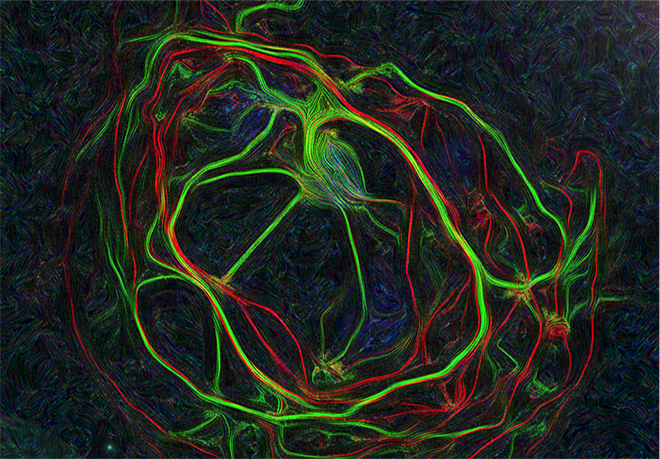
- Le transport et la traduction locale des ARNm dans l’axone de motoneurones sains et malades en utilisant des techniques de détection de molécules uniques (smFISH) ou des systèmes de marquage (MS2 ou SunTag) intégrés par CRISPR-Cas9 dans les gènes d’intérêt pour une visualisation en cellules vivantes.
- L’interactome de SMN dans des MN et des muscles sains et SMA en combinant CRISPR-Cas9 et BioID.
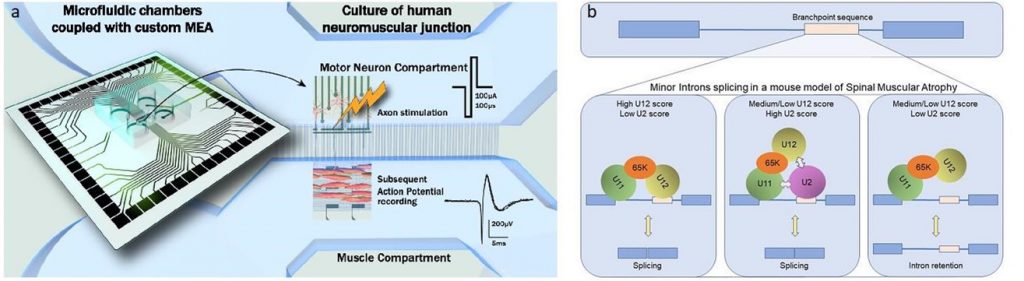
- La fonctionnalité de la NMJ mature au cours de son développement et de son maintien par l’utilisation d’un système compartimentalisé de chambres micro-fluidiques équipées d’une plateforme de microélectrodes en collaboration avec B. Charlot (IES) et Gilles Carnac (Phymedexp)
- Enfin, en collaboration avec Eran Perlson (Université de Tel Aviv, Israël), nous développons une plateforme de culture à 24 chambres microfluidiques, combinées à des MEA, dans le but de récapituler des JNM humaines de patients SMA et ALS et d’effectuer des criblages de drogues avec une approche de type médecine personnalisée.