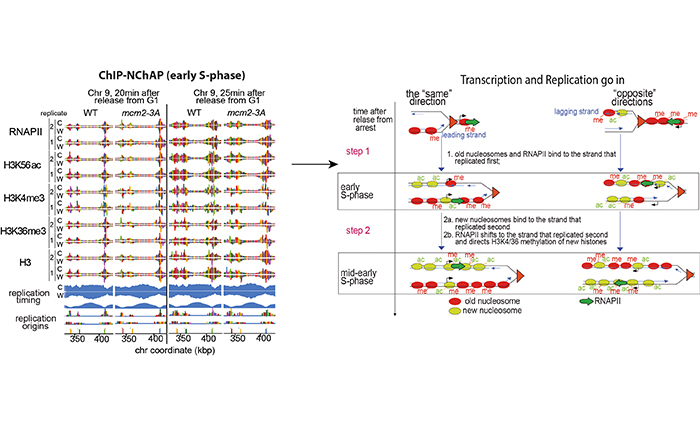
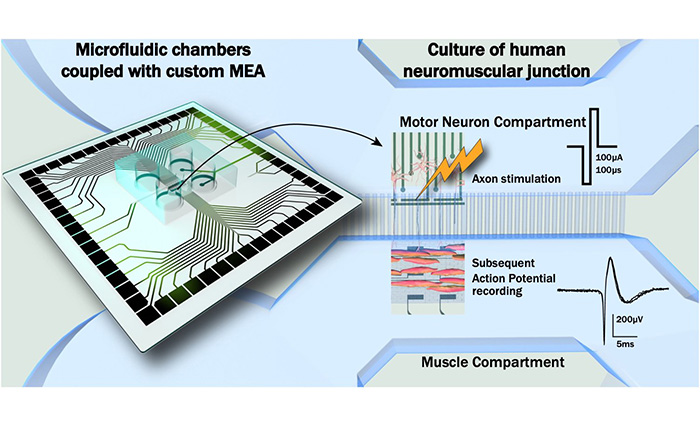
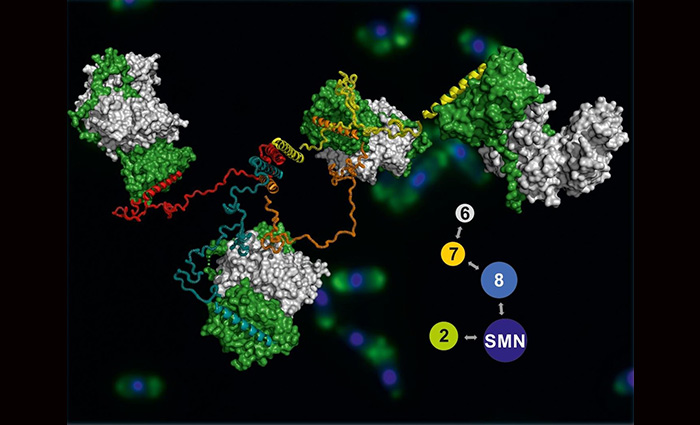
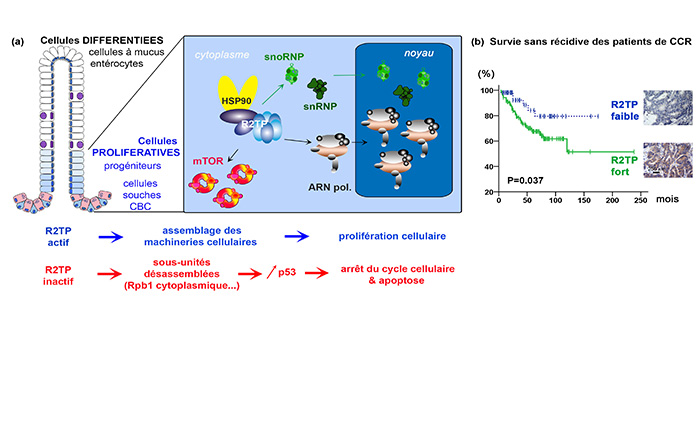
Science
LAUREAT ERC Starting grant 2021: Karim MAJZOUB
Karim MAJZOUB selected from 397 scientists for the prestigious Starting Grant from the European Research Council – ERC. The ERC Starting Grants are designed to support excellent Principal Investigators at the career stage at which they are starting their own independent research team or programme. DELV – DELta Virus infection in animal and human hosts : The emergence and rapid transmission … Continue reading LAUREAT ERC Starting grant 2021: Karim MAJZOUB
Three CNRS life scientists join the EMBO Young Investigator Network
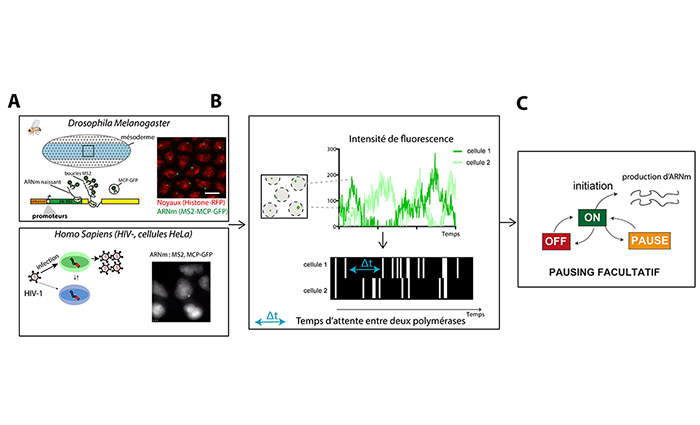
EMBO YOUNG INVESTIGATOR 2021 December 8th, 2021 – Among twenty-six life scientists, Mounia Lagha New Member of the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO) The EMBO Young Investigator Programme supports life scientists who have an excellent track record and have been group leaders for at least one but less than four years. As part of the programme, EMBO Young Investigators benefit … Continue reading Three CNRS life scientists join the EMBO Young Investigator Network
BETTENCOURT PRIZE “COUPS D’ÉLAN POUR LA RECHERCHE FRANÇAISE”
MOUNIA LAGHA LAUREATE 2021 « L’expression des gènes au cours du développement : être au bon endroit au bon moment » The prize was created by the BETTENCOURT Foundation in 2000. Since then, 74 French laboratories and more than 800 researchers have benefited from this prize. This Bettencourt prize, awarded on 23 November 2021, will be used to purchase … Continue reading BETTENCOURT PRIZE “COUPS D’ÉLAN POUR LA RECHERCHE FRANÇAISE”